BoxLang 🚀 A New JVM Dynamic Language Learn More...
WELCOME TO THE COLDBOX SECURITY MODULE
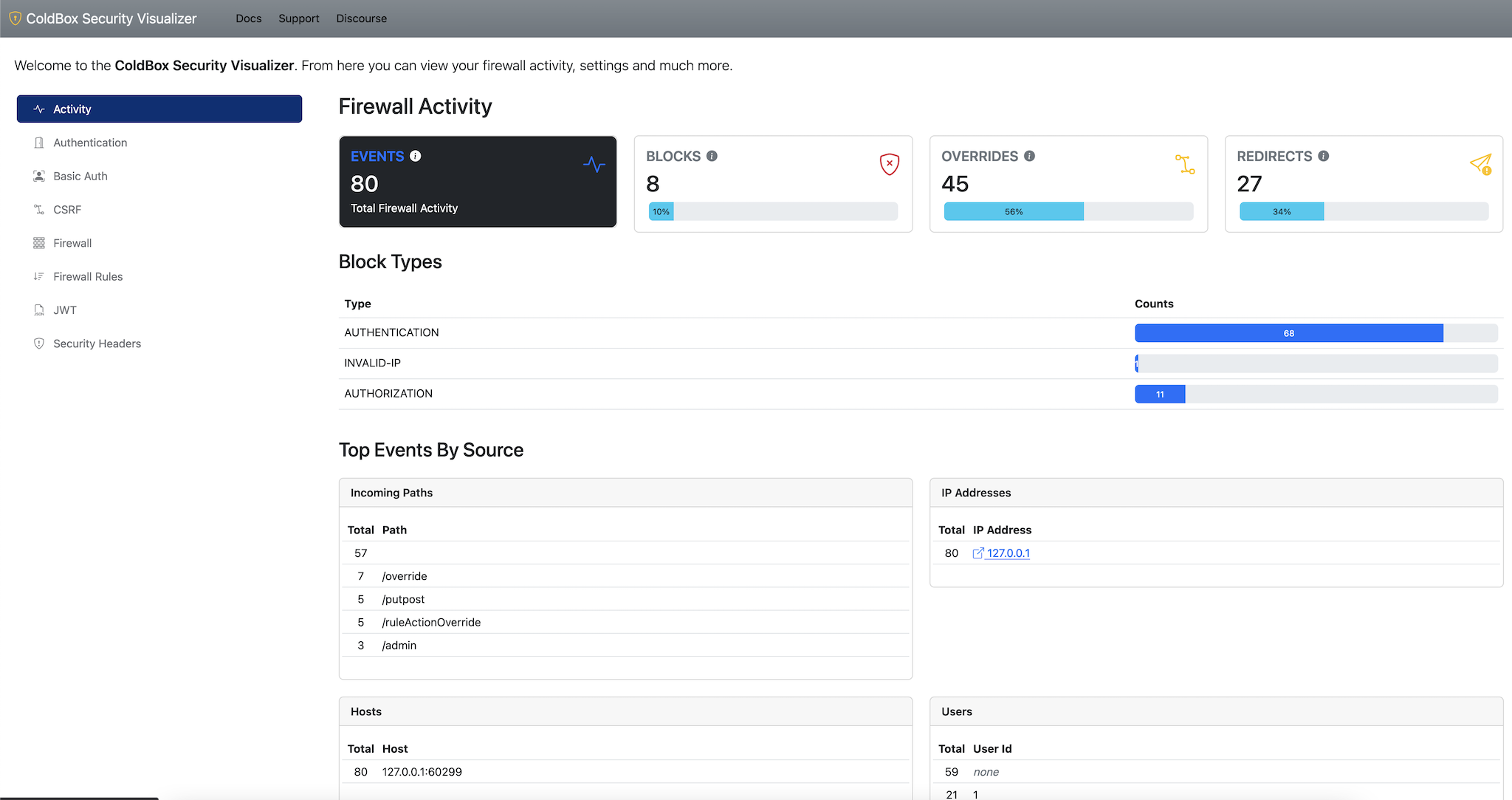
This module will enhance your ColdBox applications by providing out-of-the-box security in the form of:
- A security rule engine for incoming requests allowing blocking, authentication, and authorization checks
- Annotation-driven security for handlers and actions
- JWT (JSON Web Tokens) generator, decoder, rotation, invalidation and authentication services
- JWT Token Storage in a cache or database
- Refresh and access tokens
- Ip Blocking, Host Blocking, and much more
- CSRF protection
- Security Headers for protection against ip spoofing, host spoofing, click jacking, ssl attacks, hsts, and much more
- Pluggable with any Authentication service or can leverage cbauth by default
- Basic auth capabilities with an internal user storage
- Capability to distinguish between invalid authentication and authorization and determine the process's outcome
- Ability to load/unload security rules from contributing modules. So you can create a nice HMVC hierarchy of security
- Ability for each module to define its own
validator
Welcome to SecureLand!
License
Apache License, Version 2.0.
Links
- https://github.com/coldbox-modules/cbsecurity
- https://forgebox.io/view/cbsecurity
- https://coldbox-security.ortusbooks.com/
Requirements
- BoxLang 1+ (Preferred)
- Lucee 5+
- Adobe 2023+
- ColdBox 6+
- ColdBox 7+ for delegates and basic auth support only
Installation
Use CommandBox to install
box install cbsecurity
You can then continue to configure the firewall in your config/Coldbox.cfc.
Settings
Below are the security settings you can use for this module. Remember
you must create the cbsecurity and cbauth
structs in your ColdBox.cfc or you can create a
config/modules/cbsecurity.cfc if you are on ColdBox 7.
moduleSettings = {
cbauth = {
// This is the path to your user object that contains the credential validation methods
userServiceClass = "entities.user"
},
cbsecurity = {
/**
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Authentication Services
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Here you will configure which service is in charge of providing authentication for your application.
* By default we leverage the cbauth module which expects you to connect it to a database via your own User Service.
*
* Available authentication providers:
* - cbauth : Leverages your own UserService that determines authentication and user retrieval
* - basicAuth : Leverages basic authentication and basic in-memory user registration in our configuration
* - custom : Any other service that adheres to our IAuthService interface
*/
authentication : {
// The WireBox ID of the authentication service to use which must adhere to the cbsecurity.interfaces.IAuthService interface.
"provider" : "authenticationService@cbauth",
// WireBox ID of the user service to use when leveraging user authentication, we default this to whatever is set
// by cbauth or basic authentication. (Optional)
"userService" : "",
// The name of the variable to use to store an authenticated user in prc scope on all incoming authenticated requests
"prcUserVariable" : "oCurrentUser"
},
/**
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Basic Auth
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* These settings are used so you can configure the hashing patterns of the user storage
* included with cbsecurity. These are only used if you are using the `BasicAuthUserService` as
* your service of choice alongside the `BasicAuthValidator`
*/
basicAuth : {
// Hashing algorithm to use
hashAlgorithm : "SHA-512",
// Iterates the number of times the hash is computed to create a more computationally intensive hash.
hashIterations : 5,
// User storage: The `key` is the username. The value is the user credentials that can include
// { roles: "", permissions : "", firstName : "", lastName : "", password : "" }
users : {}
},
/**
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* CSRF - Cross Site Request Forgery Settings
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* These settings configures the cbcsrf module. Look at the module configuration for more information
*/
csrf : {
// By default we load up an interceptor that verifies all non-GET incoming requests against the token validations
enableAutoVerifier : false,
// A list of events to exclude from csrf verification, regex allowed: e.g. stripe\..*
verifyExcludes : [],
// By default, all csrf tokens have a life-span of 30 minutes. After 30 minutes, they expire and we aut-generate new ones.
// If you do not want expiring tokens, then set this value to 0
rotationTimeout : 30,
// Enable the /cbcsrf/generate endpoint to generate cbcsrf tokens for secured users.
enableEndpoint : false,
// The WireBox mapping to use for the CacheStorage
cacheStorage : "CacheStorage@cbstorages",
// Enable/Disable the cbAuth login/logout listener in order to rotate keys
enableAuthTokenRotator : true
},
/**
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Firewall Settings
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* The firewall is used to block/check access on incoming requests via security rules or via annotation on handler actions.
* Here you can configure the operation of the firewall and especially what Validator will be in charge of verifying authentication/authorization
* during a matched request.
*/
firewall : {
// Auto load the global security firewall automatically, else you can load it a-la-carte via the `Security` interceptor
"autoLoadFirewall" : true,
// The Global validator is an object that will validate the firewall rules and annotations and provide feedback on either authentication or authorization issues.
"validator" : "AuthValidator@cbsecurity",
// Activate handler/action based annotation security
"handlerAnnotationSecurity" : true,
// The global invalid authentication event or URI or URL to go if an invalid authentication occurs
"invalidAuthenticationEvent" : "",
// Default Auhtentication Action: override or redirect when a user has not logged in
"defaultAuthenticationAction" : "redirect",
// The global invalid authorization event or URI or URL to go if an invalid authorization occurs
"invalidAuthorizationEvent" : "",
// Default Authorization Action: override or redirect when a user does not have enough permissions to access something
"defaultAuthorizationAction" : "redirect",
// Firewall database event logs.
"logs" : {
"enabled" : false,
"dsn" : "",
"schema" : "",
"table" : "cbsecurity_logs",
"autoCreate" : true
},
// Firewall Rules, this can be a struct of detailed configuration
// or a simple array of inline rules
"rules" : {
// Use regular expression matching on the rule match types
"useRegex" : true,
// Force SSL for all relocations
"useSSL" : false,
// A collection of default name-value pairs to add to ALL rules
// This way you can add global roles, permissions, redirects, etc
"defaults" : {},
// You can store all your rules in this inline array
"inline" : [],
// If you don't store the rules inline, then you can use a provider to load the rules
// The source can be a json file, an xml file, model, db
// Each provider can have it's appropriate properties as well. Please see the documentation for each provider.
"provider" : { "source" : "", "properties" : {} }
}
},
/**
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Security Visualizer
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* This is a debugging panel that when active, a developer can visualize security settings and more.
* You can use the `securityRule` to define what rule you want to use to secure the visualizer but make sure the `secured` flag is turned to true.
* You don't have to specify the `secureList` key, we will do that for you.
*/
visualizer : {
"enabled" : false,
"secured" : false,
"securityRule" : {}
},
/**
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Security Headers
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* This section is the way to configure cbsecurity for header detection, inspection and setting for common
* security exploits like XSS, ClickJacking, Host Spoofing, IP Spoofing, Non SSL usage, HSTS and much more.
*/
securityHeaders : {
// Master switch for security headers
"enabled" : true,
// If you trust the upstream then we will check the upstream first for specific headers
"trustUpstream" : false,
// Content Security Policy
// Content Security Policy (CSP) is an added layer of security that helps to detect and mitigate certain types of attacks,
// including Cross-Site Scripting (XSS) and data injection attacks. These attacks are used for everything from data theft, to
// site defacement, to malware distribution.
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/CSP
"contentSecurityPolicy" : {
// Disabled by defautl as it is totally customizable
"enabled" : false,
// The custom policy to use, by default we don't include any
"policy" : ""
},
// The X-Content-Type-Options response HTTP header is a marker used by the server to indicate that the MIME types advertised in
// the Content-Type headers should be followed and not be changed => X-Content-Type-Options: nosniff
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-Content-Type-Options
"contentTypeOptions" : { "enabled" : true },
"customHeaders" : {
// Name : value pairs as you see fit.
},
// Disable Click jacking: X-Frame-Options: DENY OR SAMEORIGIN
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-Frame-Options
"frameOptions" : { "enabled" : true, "value" : "SAMEORIGIN" },
// HTTP Strict Transport Security (HSTS)
// The HTTP Strict-Transport-Security response header (often abbreviated as HSTS)
// informs browsers that the site should only be accessed using HTTPS, and that any future attempts to access it
// using HTTP should automatically be converted to HTTPS.
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Strict-Transport-Security,
"hsts" : {
"enabled" : true,
// The time, in seconds, that the browser should remember that a site is only to be accessed using HTTPS, 1 year is the default
"max-age" : "31536000",
// See Preloading Strict Transport Security for details. Not part of the specification.
"preload" : false,
// If this optional parameter is specified, this rule applies to all of the site's subdomains as well.
"includeSubDomains" : false
},
// Validates the host or x-forwarded-host to an allowed list of valid hosts
"hostHeaderValidation" : {
"enabled" : false,
// Allowed hosts list
"allowedHosts" : ""
},
// Validates the ip address of the incoming request
"ipValidation" : {
"enabled" : false,
// Allowed IP list
"allowedIPs" : ""
},
// The Referrer-Policy HTTP header controls how much referrer information (sent with the Referer header) should be included with requests.
// Aside from the HTTP header, you can set this policy in HTML.
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/Referrer-Policy
"referrerPolicy" : { "enabled" : true, "policy" : "same-origin" },
// Detect if the incoming requests are NON-SSL and if enabled, redirect with SSL
"secureSSLRedirects" : { "enabled" : false },
// Some browsers have built in support for filtering out reflected XSS attacks. Not foolproof, but it assists in XSS protection.
// https://developer.mozilla.org/en-US/docs/Web/HTTP/Headers/X-XSS-Protection,
// X-XSS-Protection: 1; mode=block
"xssProtection" : { "enabled" : true, "mode" : "block" }
},
/**
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Json Web Tokens Settings
* --------------------------------------------------------------------------
* Here you can configure the JWT services for operation and storage. In order for your firewall
* to leverage JWT authentication/authorization you must make sure you use the `JwtAuthValidator` as your
* validator of choice; either globally or at the module level.
*/
jwt : {
// The issuer authority for the tokens, placed in the `iss` claim
"issuer" : "",
// The jwt secret encoding key, defaults to getSystemEnv( "JWT_SECRET", "" )
"secretKey" : getSystemSetting( "JWT_SECRET", "" ),
// by default it uses the authorization bearer header, but you can also pass a custom one as well.
"customAuthHeader" : "x-auth-token",
// The expiration in minutes for the jwt tokens
"expiration" : 60,
// If true, enables refresh tokens, longer lived tokens (not implemented yet)
"enableRefreshTokens" : false,
// The default expiration for refresh tokens, defaults to 30 days
"refreshExpiration" : 10080,
// The Custom header to inspect for refresh tokens
"customRefreshHeader" : "x-refresh-token",
// If enabled, the JWT validator will inspect the request for refresh tokens and expired access tokens
// It will then automatically refresh them for you and return them back as
// response headers in the same request according to the customRefreshHeader and customAuthHeader
"enableAutoRefreshValidator" : false,
// Enable the POST > /cbsecurity/refreshtoken API endpoint
"enableRefreshEndpoint" : true,
// encryption algorithm to use, valid algorithms are: HS256, HS384, and HS512
"algorithm" : "HS512",
// Which claims neds to be present on the jwt token or `TokenInvalidException` upon verification and decoding
"requiredClaims" : [] ,
// The token storage settings
"tokenStorage" : {
// enable or not, default is true
"enabled" : true,
// A cache key prefix to use when storing the tokens
"keyPrefix" : "cbjwt_",
// The driver to use: db, cachebox or a WireBox ID
"driver" : "cachebox",
// Driver specific properties
"properties" : {
"cacheName" : "default"
}
}
}
}
};
Usage
This module will automatically register the Security
firewall interceptor for you according to the settings shown above and
using the interceptor => (cbsecurity.interceptor.Security).
Info You can deactivate this and load it as a manual interceptor via the
autoLoadFirewallsetting.
The interceptor will intercept all calls to your application via the
preProcess() interception point. Each request will then
be validated against registered security rules and against any active
handler/action security annotations (if active) via a Security
Validator. Also, if the request is made to a module, each module can
have its own separate validator apart from the global one.
Info You can deactivate annotation driven security via the
handlerAnnotationSecuritysetting.
How does validation happen?
How does the interceptor know a user doesn't have access? Well, here
is where you register a Validator CFC (validator setting)
with cbsecurity that implements two validation functions:
ruleValidator() and annotationValidator().
Info You can find an interface for these methods in
cbsecurity.interfaces.ISecurityValidator
The validator's job is to tell back to the firewall if they are allowed access and if they don't, what type of validation they broke: authentication or authorization or just plainly block the request.
Authenticationis when a user is NOT logged in
Authorizationis when a user does not have the proper permissions to access an event/handler or action.
Validation Process
Once the firewall has the results, and the user is NOT allowed access. Then the following will occur:
- The request will be logged via LogBox
- If the firewall database logs are enabled, then we will log it in our database logs
- The current URL will be flashed as
_securedURLso it can be used in relocations- Security Note: The URL is validated to ensure it belongs to the same host as the current request to prevent open redirect attacks
- Only same-host URLs or relative URLs are allowed; external URLs will be replaced with the application home page
- If using a rule, the rule will be stored in
prcascbsecurity_matchedRule - The validator results will be stored in
prcascbsecurity_validatorResults - If the type of invalidation is
authenticationthecbSecurity_onInvalidAuthenticationinterception will be announced - If the type of invalidation is
authorizationthecbSecurity_onInvalidAuthorizationinterception will be announced - If the type is
authenticationthe default action for that type will be executed (An override or a relocation)invalidAuthenticationEvent - If the type is
authorizationthe default action for that type will be executed (An override or a relocation)invalidAuthorizationEvent - If the action is
blockthen the firewall will block the request.
Caveats
If you are securing a module, then the module has the capability to
override the global settings if it declares them in its ModuleConfig.cfc
Security Rules
Rules can be declared in your config/ColdBox.cfc or in
any module's ModuleConfig.cfc inline, or they can come
from the following sources:
- A JSON file
- An XML file
- The database by adding the configuration settings for it
- A model by executing the
getSecurityRules()method from it
Rule Anatomy
A rule is a struct that can be composed of the following elements.
All of them are optional except the secureList.
rules = [
{
"whitelist" : "", // A list of white list events or Uri's
"securelist" : "", // A list of secured list events or Uri's
"match" : "event", // Match the event or a url
"roles" : "", // Attach a list of roles to the rule
"permissions" : "", // Attach a list of permissions to the rule
"redirect" : "", // If rule breaks, and you have a redirect it will redirect here
"overrideEvent" : "", // If rule breaks, and you have an event, it will override it
"useSSL" : false, // Force SSL,
"action" : "", // The action to use (redirect|override|block) when no redirect or overrideEvent is defined in the rule.
"module" : "", // metadata we can add so mark rules that come from modules
"httpMethods" : "*", // Match all HTTP methods or particular ones as a list
"allowedIPs" : "*" // The rule only matches if the IP list matches. It can be a list of IPs to match.
};
]
Global Rules
The global rules come from the config/Coldbox.cfc and
they are defined within the cbsecurity module setting.
// Module Settings
moduleSettings = {
// CB Security
cbSecurity : {
firewall : {
// Global Relocation when invalid access is detected, instead of each rule declaring one.
"invalidAuthenticationEvent" : "main.index",
// Global override event when invalid access is detected, instead of each rule declaring one.
"invalidAuthorizationEvent" : "main.index",
// Default invalid action: override or redirect or block when invalid access is detected, default is to redirect
"defaultAuthenticationAction" : "block",
// Default invalid action: override or redirect or block when invalid access is detected, default is to redirect
"defaultAuthorizationAction" : "redirect",
// The global security rules as inline
"rules" : [
// should use direct action and do a global redirect
{
"whitelist": "",
"securelist": "admin",
"match": "event",
"roles": "admin",
"permissions": "",
"action" : "redirect"
},
// no action, use global default action
{
"whitelist": "",
"securelist": "noAction",
"match": "url",
"roles": "admin",
"permissions": ""
},
// Using overrideEvent only, so use an explicit override
{
"securelist": "ruleActionOverride",
"match": "url",
"overrideEvent": "main.login"
},
// direct action, use global override
{
"whitelist": "",
"securelist": "override",
"match": "url",
"roles": "",
"permissions": "",
"action" : "override"
},
// Using redirect only, so use an explicit redirect
{
"securelist": "ruleActionRedirect",
"match": "url",
"redirect": "main.login"
}
]
}
}
};
Module Rules
Module rules come from the ModuleConfig.cfc by creating
a cbSecurity key in the module's settings struct:
// module settings - stored in modules.name.settings
settings = {
// CB Security Rules to append to global rules
cbsecurity = {
firewall : {
// Module Relocation when an invalid access is detected, instead of each rule declaring one.
"invalidAuthenticationEvent" : "mod1:secure.index",
// Default Authentication Action: override or redirect or block when a user has not logged in
"defaultAuthenticationAction" : "override",
// Module override event when an invalid access is detected, instead of each rule declaring one.
"invalidAuthorizationEvent" : "mod1:secure.auth",
// Default Authorization Action: override or redirect or block when a user does not have enough permissions to access something
"defaultAuthorizationAction" : "override",
// Custom validator for the module.
"validator" : "JwtAuthValidator@cbsecurity"
// You can define your security rules here or externally via a source
"rules" : [
{
"secureList" : "mod1:home"
},
{
"secureList" : "mod1/modOverride",
"match" : "url",
"action" : "override"
}
]
}
}
};
Annotation Security
The firewall will inspect handlers for the secured
annotation. This annotation can be added to the entire handler, an
action, or both. The default value of the secured
annotation is a boolean true. This means we need a user
to be authenticated to access it.
// Secure this handler
component secured{
function index(event,rc,prc){}
function list(event,rc,prc){}
}
// Same as this
component secured=true{
}
// Not the same as this
component secured=false{
}
// Or this
component{
function index(event,rc,prc) secured{
}
function list(event,rc,prc) secured="list"{
}
}
Authorization Context
You can also give the annotation some value, which can be anything you like: A list of roles, a role, a list of permissions, metadata, etc. Whatever it is, this is the authorization context, and the security validator must be able to not only authenticate but authorize the context, or an invalid authorization will occur.
// Secure this handler
component secured="admin,users"{
function index(event,rc,prc) secured="list"{
}
function save(event,rc,prc) secured="write"{
}
}
Cascading Security
By annotating the handler and the action, you create a cascading security model where they need to be able to access the handler first, and only then will the action be evaluated for access.
Security Validator
Now that we have seen security rules and annotations let's see how to
validate them. Create a CFC or use any CFC in your models
and add the following functions: ruleValidator() and annotationValidator()
/**
* This function is called once an incoming event matches a security rule.
* You will receive the security rule that matches and an instance of the ColdBox controller.
*
* You must return a struct with the following keys:
* - allow:boolean True, user can continue access, false, invalid access actions will ensue
* - type:string(authentication|authorization) The type of block that ocurred. Either an authentication or an authorization issue.
* - messages:string Any messages for debugging
*
* @return { allow:boolean, type:string(authentication|authorization), messages:string }
*/
struct function ruleValidator( required rule, required controller );
/**
* This function is called once access to a handler/action is detected.
* You will receive the secured annotation value and an instance of the ColdBox Controller
*
* You must return a struct with the following keys:
* - allow:boolean True, user can continue access, false, invalid access actions will ensue
* - type:string(authentication|authorization) The type of block that ocurred. Either an authentication or an authorization issue.
* - messages:string Any messages for debugging
*
* @return { allow:boolean, type:string(authentication|authorization), messages:string }
*/
struct function annotationValidator( required securedValue, required controller );
Each validator must return a struct with the following keys:
-
allow:booleanA boolean indicator if authentication or authorization was violated -
type:stringOf(authentication|authorization)A string that indicates the type of violation: authentication or authorization. -
messages:stringA string of messages used for debugging
Here is a sample validator using permission-based security in both rules and annotation context
struct function ruleValidator( required rule, required controller ){
return permissionValidator( rule.permissions, controller, rule );
}
struct function annotationValidator( required securedValue, required controller ){
return permissionValidator( securedValue, controller );
}
private function permissionValidator( permissions, controller, rule ){
var results = { "allow" : false, "type" : "authentication", "messages" : "" };
var user = security.getCurrentUser();
// First check if user has been authenticated.
if( user.isLoaded() AND user.isLoggedIn() ){
// Do we have the right permissions
if( len( arguments.permissions ) ){
results.allow = user.checkPermission( arguments.permission );
results.type = "authorization";
} else {
results.allow = true;
}
}
return results;
}
Interceptions
Authentication / Authorization
When invalid access or authorizations occur, the interceptor will announce the following events:
-
cbSecurity_onInvalidAuthentication- When an invalid authentication is detected -
cbSecurity_onInvalidAuthorization- When an invalid authorization is detected
You will receive the following data in the interceptData struct:
-
ip: The offending Ip address -
rule: The security rule intercepted or empty if annotations -
settings: The firewall settings -
validatorResults: The validator results -
annotationType: The annotation type intercepted,handleroractionor empty if rule driven -
processActions: A boolean indicator that defaults to true. If you change this to false, then the interceptor won't fire the invalid actions. Usually this means, you manually will do them.
Firewall Blocks
-
cbSecurity_onFirewallBlock- When the firewall blocks an incoming request with a 403
You will receive the following data in the interceptData struct:
-
type: The type of block:hostheaderoripvalidation -
config: The configuration structure of the rule -
incomingIP: The incoming ip if the type isipValiation -
incomingHost: The incoming host if the type ishostHeader
Security Visualizer
This module also ships with a security visualizer that will document
all your security rules and settings in a nice panel. In order to
activate it you must add the visualizer setting to your
config and mark it as enabled. Once enabled you can
navigate to: /cbsecurity, and you will be presented with
the visualizer.
Important The visualizer is disabled by default

Running Tests and Contributing
Please read our Contributing guide first.
To run the tests, start one of the servers from the
/test-harness directory.
You will also need a MySQL database seeded with the
/test-harness/tests/resources/cbsecurity.sql file. Docker
makes this a cinch:
docker run -d \
--name=cbsecurity \
-p 3306:3306 \
-e MYSQL_ROOT_PASSWORD=mysql \
-e MYSQL_DATABASE=cbsecurity \
-v $(pwd)/test-harness/tests/resources/cbsecurity.sql:/docker-entrypoint-initdb.d/cbsecurity.sql \
mysql:5
Finally, run the tests by visiting your server's
/tests/runner.cfm file.
Copyright Since 2005 ColdBox Framework by Luis Majano and Ortus Solutions, Corp www.coldbox.org | www.luismajano.com | www.ortussolutions.com
HONOR GOES TO GOD ABOVE ALL
Because of His grace, this project exists. If you don't like this, then don't read it, it's not for you.
"Therefore being justified by faith, we have peace with God through our Lord Jesus Christ: By whom also we have access by faith into this grace wherein we stand, and rejoice in hope of the glory of God. And not only so, but we glory in tribulations also: knowing that tribulation worketh patience; And patience, experience; and experience, hope: And hope maketh not ashamed; because the love of God is shed abroad in our hearts by the Holy Ghost which is given unto us. ." Romans 5:5
THE DAILY BREAD
"I am the way, and the truth, and the life; no one comes to the Father, but by me (JESUS)" Jn 14:1-12
Changelog
All notable changes to this project will be documented in this file.
The format is based on Keep a Changelog, and this project adheres to Semantic Versioning.
Unreleased
3.7.0 - 2026-01-14
Changed
- Increased VARCHAR field sizes in
DBLoggertable schema to accommodate longer URLs and user agent strings. Fieldshost,path,queryString,referer, anduserAgentnow use VARCHAR(1024) to prevent truncation of data. - Updated
DBLoggerinsert statements to truncatehost,path,queryString,referer, anduserAgentvalues to 1024 characters usingleft()function to prevent database errors.
Fixed
- Allow for sub-modules to load AFTER cbsecurity loads.
- Make sure the jwt token is not null when doing discovery in the JwtService.
- Fixed
isSafeRedirectUrl()host comparison for non-default ports by stripping port from host before comparing with URI host. - ACF Compatibility: Fixed
dateTimeFormatusage forlogDatein activity view to prevent conversion errors in Adobe ColdFusion.
Added
- Added
TokenRejectionExceptionhandling in JWT handler to properly handle token rejection errors. - Updated JWT handler error message calls to match specification.
- Added test cases for non-default port scenarios in
isSafeRedirectUrl()validation. - Added test validation for JWT response messages.
3.6.0 - 2025-12-08
Security
- CRITICAL: Fixed open redirect vulnerability in
_securedURLhandling. ThesaveSecuredUrl()method now validates redirect URLs to ensure they belong to the same host as the current request, preventing attackers from crafting malicious URLs that redirect users to external sites after login. AddedisSafeRedirectUrl()validation usingjava.net.URIto compare hosts.
Fixed
- BOX-164 Allow Visualizer to show settings when firewall.logging not enabled
- JWT Handler improperly returns a value causing it to skip ColdBox's RestHandler's response formatting logic. This results in the entire response object being returned rather than just invoking getDataPacket()
3.5.0 - 2025-10-17
Added
- Upgraded test harness
- BoxLang certification
- Github Actions updates
- ColdBox 8 Support and certification
- Added
.github/copilot-instructions.md— concise AI-agent guidance covering module architecture, validators, interceptor flows, and developer workflows (install, test, server start). - Documented test-harness and TestBox runner details for local integration testing (see
test-harness/tests/runner.cfmandbox.jsonscripts).
3.4.3 - 2024-05-09
Fixed
- Renamed
renderView()toviewto be ColdBox 7 compliant now.
3.4.2 - 2024-01-10
Fixed
- Markdown rules updated to fix duplicate headers
- Updated security logs columns to work in Oracle as
clob cbsecurity_logsis hard coded instead of using module setting
3.4.1 - 2023-08-09
Fixed
- Parenthesis on
topstatements for MSSQL Server on theDBLoggerthanks to @irvirv
3.4.0 - 2023-06-14
Added
- Official Adobe 2023 Support
- Gitflows for testing all engines and all versions of ColdBox
- Added
transientCache=falseto authUserto avoid any issues when doing security operations - Added population control for auth
Userfor extra security
Fixed
Userauth was not serializing theidof the user in the mementifier config
[3.3.0] => 2023-MAR-31
Added
- Added
guest()method to CBSecurity model andAuthorizabledelegate
[3.2.0] => 2023-MAR-29
Added
- Migrations table for security logs
- New bootsrap icons + css + js
- New github support files
Fixed
getActionsReport()was not defaulting the type's structure, so exceptions would arise when there was no data in the visualizer
[3.1.0] => 2023-FEB-17
Added
- Added a new helper:
createPassword()on theCBSecuritymodel to generate secure, random passwords with letters, symbols and numbers. cbcsrfupgraded to version 3, we missed in the previous release.
[3.0.0] => 2023-JAN-17
Changed / COMPATIBILITY
- Dropped ACF2016
- Separated routes to it's own module Router
- COMPAT New
JwtAuthValidatorinstead of mixing concerns with theJwtService. You will have to update your configuration to use thisvalidatorinstead of theJwtService useSSLis now defaulted totruefor all security relocations as the default- Encapsulation of
jwtsettings from theModuleConfigto theJwtService CBAuthValidatorhas been renamed to justAuthValidatorthis way it can be used with ANY authentication service instead of binding it to justcbauth. This validator just relies on theIAuthUserinterface now.
Added
- New
AuthValidatornow can validate permissions and roles according to ourIAuthUserinterface but can be used on ANY authentication service that implementsIAuthService - New authorization and authentication delegates for usage in cb7
- New ability for the firewall to log all action events to a database table.
- New visualizer that can visualize all settings and all firewall events via the log table if enabled.
- New Basic Auth validator and basic auth user credentials storage system. This will allow you to secure your apps where no database interaction is needed or required.
- New global and rule action:
blockand the fireall will block the request with a 401 Unathorized page. - New event
cbSecurity_onFirewallBlockannounced whenever the firewall blocks a request into the system with a 403. DBTokenStoragenow rotates using async scheduler and not direct usage anymore.- Ability to set the
cbcsrfmodule settings into thecbsecuritysettings ascsrf. - We now default the user service class and the auth token rotation events according to used authentication service (cbauth, etc), no need to duplicate work.
- New rule based IP security. You can add a
allowedIPskey into any rule and add which IP Addresses are allowed into the match. By default, it matches all IPs. - New rule based HTTP method security. You can add a
httpMethodskey into any rule and add which HTTP methods are allowed into the match. By default, it matches all HTTP Verbs. - New
securityHeadersconfiguration to allow a developer to protect their apps from common exploits: xss, HSTS, Content Type Options, host header validation, ip validation, click jacking, non-SSL redirection and much more. - Authenticated user is now stored by the security firewall according to the
prcUserVariableon authenticated calls viapreProcess()no matter the validator used - Dynamic Custom Claims: You can pass a function/closure as the value for a custom claim and it will be evaluated at runtime passing in the current claims before being encoded
- Allow passing in custom refresh token claims to
attempt()andfromUser()andrefreshToken():refreshCustomClaims - Added
TokenInvalidExceptionandTokenExpiredExceptionto therefreshTokenendpoint
Fixed
- Disable lastAccessTimeouts for JWT CacheTokenStorage BOX-128
- Fix spelling of property
datasourceon queryExecute that was causing a read issue.
[2.15.0] => 2021-DEC-10
🚀 Added
- Pass custom claims from
refreshToken( token, customClaims)method when refreshing tokens - Pass in the current jwt payload in to
getJWTCustomClaims( payload ) - The auto refresh token features now will auto refresh not only on expired tokens, but on invalid and missing tokens as well. Thanks to @elpete
🐛 Fixed
- Timeout in token storage is now the token timeout
[2.14.0] => 2021-OCT-07
Added
threadsafeannotation to all models to prevent invalid creations under load, since we don't use circular dependencies.
[2.13.0] => 2021-SEP-02
Added
- Adobe 2021 Support
- Migration to github actions from travis
- Refresh tokens support
- Refresh token endpoint
/cbsecurity/refreshtTokenfor secure refresh token generation - Manual refresh token method on the
JwtService:refreshToken( token ) - Auto refresh token header interceptions for JWT validators
- Detect on
authenticate()if the payload is empty and throw the appropriate exceptions - Added ability for the
authenticate( payload )to receive a payload to authenticate - Added ability to recreate the token storage using a
forceargumentgetTokenStorage( force = false ) - Ability for the
parseToken()to choose to store and authenticate or just parse
Changed
- The
IAuthUserno longer requires theisLoggedIn()method. This is now fully optional.
Fixed
- Unique
jticould have collisions if tokens created at the same time, add randomness to it TokenExpirationExceptionnot relaeyed from the base jwt library- If
variables.settings.jwt.tokenStorage.enabledis disabled all invalidations failed, make sure if the storage is disabled to not throw storage exceptions.
[2.12.0] => 2021-MAR-29
Added
- More and more apps will need real ip's from request, so expose it via the
CBSecuritymodel service as :getRealIp()
Fixed
- When using
getHTTPREquestData()sendfalseso we DON'T retrieve the http body when we just need the headers - More updates to
getRealIp()when dealing with lists
[2.11.1] => 2021-MAR-10
Fixed
- Fix
getRealIP()to only return originating user's source IP, if the forwarded ip is a list
[2.11.0] => 2021-MAR-10
Added
- Add a
secureSameUsermethod to throw when passed a different user #29 (https://github.com/coldbox-modules/cbsecurity/pull/29)
[2.10.0] => 2021-FEB-12
Added
- Moved the registration of the validator from the
configure()to theafterAspectsLoad()interception point to allow for modules to declare the validator if needed. - Moved handler bean to
afterAspectsLoad()to allow for module based invalid events to work.
[2.9.0] => 2020-DEC-11
Fixed
- Fixes a typo in the
cbSecurity_onInvalidAuthorizationinterception point declaration. Previously, the typo would prevent ColdBox from allowing the correctly-typed interception point from ever triggering an interception listener. - The
userValidator()method has been changed toroleValidator(), but the error message was forgotten! So the developer is told they need auserValidator()method... because theuserValidatormethod is no longer supported. :/
Added
- The
isLoggedIn()method now makes sure that a jwt is in place and valid, before determining if you are logged in or not. - Migrated all automated tests to
focalandmysql8in preparation for latest updates - Add support for JSON/XML/model rules source when loading rules from modules. Each module can now load rules not only inline but from the documented external sources.
- Ensure non-configured
rulesdefault to empty array
[2.8.0] => 2020-NOV-09
Added
parseToken( token )now accepts a token of your choice to work with in the request or it will continue to discover it if not passed.- Added new JWT Service method:
invalidateAll()which invalidates all tokens in the token storage - Added the new event:
cbSecurity_onJWTInvalidateAllTokensthat fires once all tokens in the storage are cleared - Added storage of the authenticated user into the
prcscope when usingattempt()to be consistent with API calls
Fixed
- Spelling corrections on the readme
- Added full var scoping for
cbsecurityin JWTService calls
[2.7.0] => 2020-SEP-14
Added
- Contributed module rules are now pre-pended instead of appended. (@wpdebruin)
Fixed
- Not loading rules by source file detection due to invalid setting check
- Don't trigger ColdBox's invalid event looping protection. It also auto-senses between ColdBox 6 and 5 (@homestar9)
- Fixed token scopes according to JWT spec, it is called
scopeand it is a space separated list. This doesn't change the User interface for it. (@wpdebruin) - Update token storages so no token rejection anymore when storage is not enabled. (@wpdebruin)
[2.6.0] => 2020-JUL-22
Added
- New build layout based on new module layout
- Auto github publishing release notes
- More formatting goodness and watcher
Fixed
- JWT Validator now passing
permissionsinstead ofroles - Token Storage checking was being done even if disabled
[2.5.0] => 2020-APR-03
Feature: Upgraded tocbAuth@ 5.x
[2.4.0] => 2020-APR-02
Feature: We now include thecbcsrfmodule to allow for protections of cross site request forgery vectors. Please see all the features included in this module here: https://github.com/coldbox-modules/cbcsrf
[2.3.0] => 2020-MAR-30
FeatureIntroduction of the cbSecurity model: https://coldbox-security.ortusbooks.com/intro/release-history/whats-new-with-2.3.0Task: Cfformatting everywhere
[2.2.1] => 2020-FEB-26
bug:verifyshould passverify=trueinto the jwt library for proper verification
[2.2.0] => 2020-FEB-12
Feature: Migrated from the jwt to thejwtcfml(https://forgebox.io/view/jwt-cfml) library to expand encoding/decoding capabilities to supportRSandESalgorithms:- HS256
- HS384
- HS512
- RS256
- RS384
- RS512
- ES256
- ES384
- ES512
Feature: Added a new convenience method on the JWT Service:isTokenInStorage( token )to verify if a token still exists in the token storageFeature: If no jwt secret is given in the settings, we will dynamically generate one that will last for the duration of the application scope.Feature: New setting forjwtstruct:issuer, you can now set the issuer of tokens string or if not set, then cbSecurity will use the home page URI as the issuer of authority string.Feature: All tokens will be validated that the sameiss(Issuer) has granted the tokenImprove: Ability to have defaults for all JWT settings instead of always typing them in the configsImprove: More cfformating goodness!Bug: Invalidation of tokens was not happening due to not using the actual key for the storage
[2.1.0] => 2019-OCT-02
Feature: cbauth upgraded to version 4
[2.0.0] => 2019-SEP-25
New Features
- Adobe 2016,2018 Support
- Settings transferred to ColdBox 4/5
moduleSettingsapproach instead of root approach (See compat section) - The
rulesModelMethodnow defaults togetSecurityRules() - ColdFusion security validator has an identity now
CFValidator@cbsecurityinstead of always being inline. - You can now add an
overrideEventelement to a rule. If that is set, then we will override the incoming event viaevent.overrideEvent()instead of doing a relocation using theredirectrule element. - You can now declare your rules inline in the configuration settings using the
ruleskey. This will allow you to build the rules in your config instead of a rule source. - We now can distinguish between invalid auth and invalid authorizations
- New interception block points
cbSecurity_onInvalidAuthentication,cbSecurity_onInvalidAuhtorization - You now have a
defaultAuthorizationActionsetting which defaults toredirect - You now have a
invalidAuthenticationEventsetting that can be used - You now have a
defaultAuthenticationActionsetting which defaults toredirect - You now have a
invalidAuthorizationEventsetting that can be used - If a rule is matched, we will store it in the
prcascbSecurity_matchedRuleso you can see which security rule was used for processing invalid access actions. - If a rule is matched we will store the validator results in
prcascbSecurity_validatorResults - Ability for modules to register cbSecurity rules and setting overrides by registering a
settings.cbSecuritykey. - Ability for modules to override the
validatorsetting. So each module can have their own security validator schema. - New security rule visualizer for graphically seeing you rules and configuration. Can be locked down via the
enableSecurityVisualizersetting. Disabled by default.
// module settings - stored in modules.name.settings
settings = {
// CB Security Rules to append to global rules
cbsecurity = {
// The module invalid authentication event or URI or URL to go if an invalid authentication occurs
"invalidAuthenticationEvent" : "",
// Default Auhtentication Action: override or redirect when a user has not logged in
"defaultAuthenticationAction" : "redirect",
// The module invalid authorization event or URI or URL to go if an invalid authorization occurs
"invalidAuthorizationEvent" : "",
// Default Authorization Action: override or redirect when a user does not have enough permissions to access something
"defaultAuthorizationAction" : "redirect",
// You can define your security rules here or externally via a source
"rules" : [
{
"secureList" : "mod1:home"
},
{
"secureList" : "mod1/modOverride",
"match" : "url",
"action" : "override"
}
]
}
};
- Annotation based security for handlers and actions using the
securedannotation. Which can be boolean or a list of permissions, roles or whatever you like. - You can disable annotation based security by using the
handlerAnnotationSecurityboolean setting.
Improvements
- SSL Enforcement now cascades according to the following lookup: Global, rule, request
- Interfaces documented for easier extension
interfaces.* - Migration to script and code modernization
- New Module Layout
- Secured rules are now logged as
warn()with the offending Ip address. - New setting to turn on/off the loading of the security firewall:
autoLoadFirewall. The interceptor will auto load and be registered ascbsecurity@globalin WireBox.
Compat
- Adobe 11 Dropped
- Lucee 4.5 Dropped
- Migrate your root
cbSecuritysettings in yourconfig/ColdBox.cfcto inside themoduleSettings - IOC rules support dropped
- OCM rules support dropped
validatorModeldropped in favor of justvalidatorto be a WireBox Id- Removed
preEventSecurityit was too chatty and almost never used - The function
userValidatorhas been renamed toruleValidatorand also added theannotationValidatoras well. rulesSourceremoved you can now use therulessetting- The
rulescan be:array, db, model, filepath - If the
filepathhasjsonorxmlin it, we will use that as the source style
- The
rulesFileremoved you can now use therulessetting.
[1.3.0]
- Travis integration
- DocBox updates
- Build process updates
[1.2.0]
- Updated documentation
- Updated doc references
- New docs build process
- Update root builder dependencies
[1.1.0]
- Updated documentation
- Ability for interceptor to auto-register via new
cbsecuritysettings in master config.
[1.0.2]
- Removed
getPlugin()deprecated calls to new approach. - https://ortussolutions.atlassian.net/browse/CCM-26 cbsecurity ocm rules not ColdBox 4 compat
[1.0.1]
- Fixed missing
$throw()method to nativethrow()method.
[1.0.0]
- Created first module version
-
Luis Majano
- Published
-
3.7.0+9 is the latest of 64 release(s)
Published
- Published on {{ getFullDate("2026-01-14T21:04:13Z") }}
-
-
Apache2
- coldbox-modules/cbsecurity
Use It
$
box install cbsecurity
Collaborators 0
Stats
- {{ getFullDate("2014-04-30T20:20:56Z") }}
- {{ getFullDate("2026-01-14T21:04:13Z") }}
- 27,187
- 500,048